At-a-glance visuals #
A quick peek at how we calibrate the score and why interpretable cues matter.
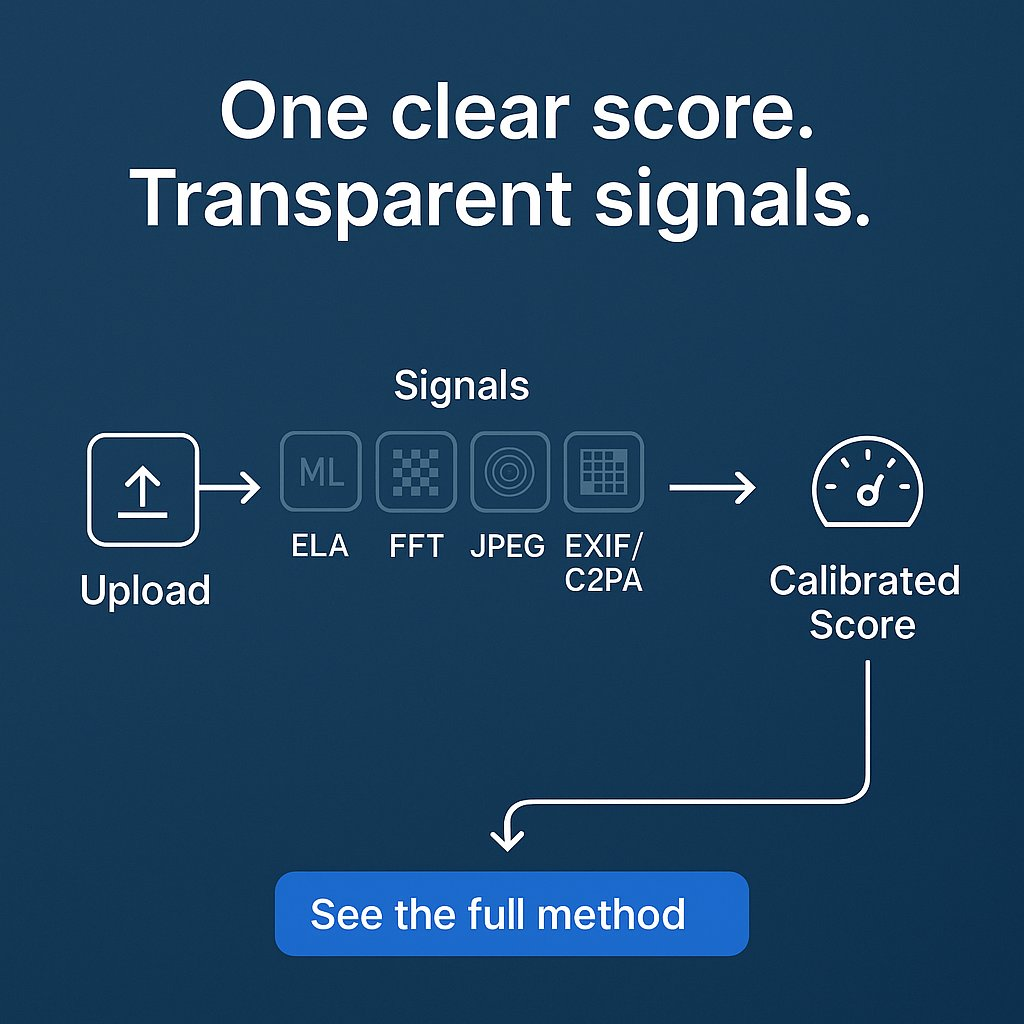
Ensemble at a glance #
We compute several detector scores and fuse them into one overall estimate. The ensemble currently includes:
- Our ML image model (live): calibrated classifier over engineered and deep features.
- Our ML text model (live): a supervised block classifier that powers the paragraph heatmap for documents.
- Media forensics: ELA, FFT-based texture analysis, JPEG grid/cues, EXIF/C2PA checks.
- Platform metadata signal (video): lightweight parsing of creator/title/description/tags for declared “AI-generated” hints.
Scores are combined with weights and confidence into a single probability. We keep the breakdown visible so you can see why a result moved up or down.
Images #
- In-house ML (primary): image-level features + calibrated forensics.
- ELA to highlight recompression anomalies.
- FFT to surface periodic textures.
- JPEG cues including block/grid behavior and chroma handling.
- Metadata & provenance (EXIF presence/consistency; surface C2PA if present).
Video — what we do (developer view) #
- Segment selection: for social URLs (YouTube/TikTok) we fetch four segments, one per quarter of the timeline (Q1–Q4). This gives broad coverage on long videos without scraping everything.
- Codec sanitization: downloaded segments are re-encoded with FFmpeg to H.264 (yuv420p, ~1s GOP, scene-cut disabled). This removes mid-GOP artifacts that can break frame seeking and avoids decoder warnings.
- Frame sampling: we read the stitched clip and sample up to ~2 fps, with a duration-aware target (≈16–40 frames depending on clip length). After each seek we discard a few “warm-up” frames to avoid residual corruption.
- Diversity filter: frames are kept only if their HSV histogram distance clears a threshold (Bhattacharyya > 0.22). This yields distinct frames across scene changes, not near-duplicates.
- Per-frame analysis: each frame runs through the same image pipeline (our ML model + forensics + EXIF-style cues where applicable).
- Metadata signal: we scan video metadata (title/description/tags/uploader) for declared AI markers (e.g., “AI-generated”, tool names, #aivideo). If present, it contributes a modest positive weight as “Platform AI label”.
- Aggregation: for each detector we take the median across frames, then blend detectors with weights and confidence using a calibrated sigmoid. The top contributing signals are exposed in the UI.
Text #
Documents are processed with an ML block classifier trained on real and AI-written samples. We split the text into small blocks, score each block, and then:
- Overall score: a calibrated blend of block scores summarises the document.
- Estimated AI-written fraction: the share of blocks that exceed our “AI-like” threshold (≥ 60%).
- Paragraph heatmap: each paragraph gets a score by overlap-weighting the ML block scores inside it.
If the ML text model is unavailable, we fall back to a heuristic analysis (burstiness, repetition, TTR, punctuation, entropy), but ML is used whenever possible.
Web & mixed content #
For URLs and documents, we extract embedded media/text and run the appropriate detectors. As we expand ML coverage, web, audio, and mixed content will receive specialized models.
How we combine signals #
Each detector outputs a score and confidence. We weight contributions and blend them into an overall probability, then calibrate. Image ML carries a strong weight; text ML for documents; forensic and metadata signals act as corroboration. Strong camera provenance (e.g., consistent EXIF) can counterbalance AI-like cues.
Interpretation #
Outputs are probabilistic—not definitive. Combine detector signals with context, source credibility, and any available provenance. For borderline cases, review the per-signal breakdown and paragraph heatmap shown in the app.